Ever thought about where Morocco really is? Finding out can be a bit tricky because of the complex world of continents. When you ask, “Is Morocco in Africa?” the answer is yes, but it’s more than that.
Morocco offers the traveler a beautiful fusion of Africa’s diverse cultures, landscapes, and soul. It’s more than a destination — it’s an experience.
James Campbell, Global Tourist
Morocco is at the northwest corner of Africa, right by the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. This spot makes it a special place where African and European cultures meet. Knowing where Morocco is tells a story that goes beyond just being in Africa.
Key Takeaways
- Morocco is geographically located in North Africa
- The country spans both African and Mediterranean regions
- Morocco borders two major bodies of water: Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea
- Its location provides unique cultural and strategic advantages
- Morocco represents a complex geographical identity bridging multiple regions
Understanding Morocco’s Geographic Position
Exploring where is Morocco reveals a fascinating crossroads. It connects multiple worlds. Located in the northwestern corner of Africa, Morocco is at a unique spot. It bridges continents and cultures.
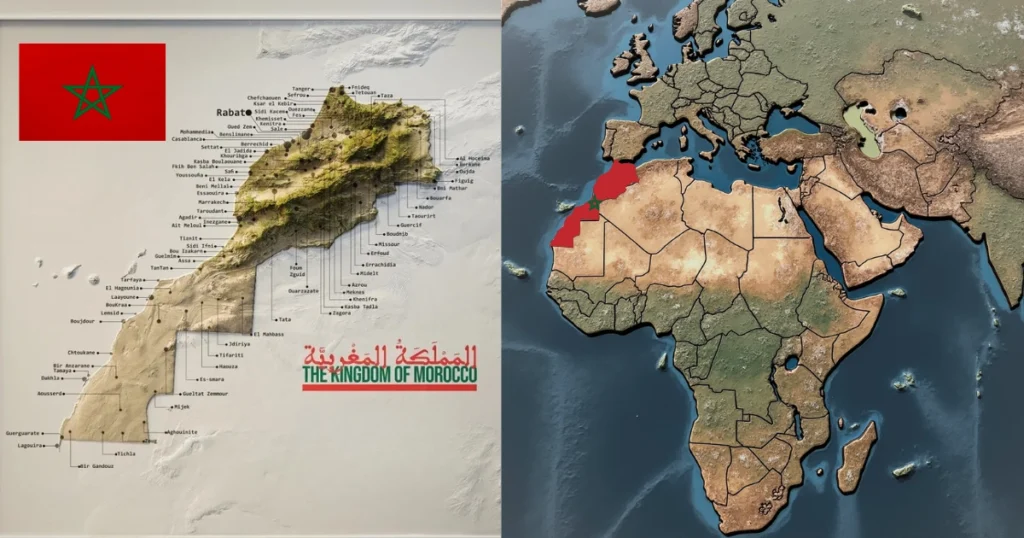
A map of Morocco shows its remarkable position. It’s nestled between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. This location gives Morocco great strategic importance. It’s a key gateway between Africa and Europe.
The North African Gateway
Morocco’s location offers several advantages:
- Direct access to the Strait of Gibraltar
- Proximity to the European mainland
- Connection between African and European trade routes
Strategic Location Between Continents
The country’s position allows for unique cultural and economic interactions. Geographically speaking, Morocco sits at a critical intersection. This has shaped its historical and contemporary significance.
Borders and Neighboring Countries
Morocco shares borders with:
- Algeria to the east
- Mauritania to the south
This strategic positioning makes Morocco a key player in regional geopolitics. It offers unique opportunities for cultural exchange and economic development.
Is Morocco in Africa? The Simple Answer
When you ask, “Is Morocco in Africa?” the answer is a clear yes. Morocco is in the northwestern part of Africa. It sits at a unique spot that often makes people curious about its place in the world.
Where is Morocco located exactly? It’s a North African country that connects Africa and Europe. It’s by the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea, linking two continents.
- Continent: Africa (specifically North Africa)
- Region: Northwestern African coast
- Geographic coordinates: 32°N, 5°W
Many people are curious about Morocco’s place because of its ties to Africa and the Arab world. Its closeness to Spain and deep Mediterranean influences make its story complex. This makes Morocco a unique spot.
| Geographic Detail | Specific Information |
|---|---|
| Continent | Africa |
| Subregion | North Africa |
| Bordering Continents | Africa, with close proximity to Europe |
Knowing Morocco’s African roots helps us understand its culture and role in the world. Its location is not just a fact, but shows the diverse connections that make this nation special.
Morocco’s Unique Continental Identity
Exploring where Morocco is in Africa reveals a nation with a rich cultural mix. Morocco is a crossroads of civilizations, blending African, Arab, and Berber influences. This creates a unique cultural tapestry.
The country’s location makes it more than just an African nation. Yes, Morocco is in Africa. But its identity goes beyond simple geography.
Cultural Fusion of African and Arab Influences
Morocco’s culture is a deep blend of traditions. Its heritage includes:
- Berber indigenous roots
- Arab linguistic and religious influences
- African tribal traditions
- Mediterranean cultural exchanges
Historical Connections to Multiple Regions
For centuries, Morocco has been a hub of cultural exchange. Its strategic location made it a bridge between Africa, Europe, and the Middle East. This created a unique multicultural environment.
Modern Day Geographic Classification
In today’s world, Morocco is seen as an African nation. It plays a role in:
- African Union
- Economic Community of West African States
- North African regional organizations
This complex identity makes Morocco a fascinating example of cultural complexity in Africa.
Exploring Morocco’s Physical Geography
Looking at a map of Morocco, you’ll see a diverse landscape. The country’s geography is a mix of coastlines, mountains, and deserts. This mix gives Morocco its special character.
When you find out where Morocco is, you’ll see its amazing geography. It stretches across Northwest Africa. Morocco’s landscape is dramatic, covering many different environments.
- Mediterranean coastline characterized by its stunning beauty and diverse ecosystems
- Rif Mountains in the north
- Atlas Mountain range cutting through the country’s interior
- Sahara Desert extending across the southeastern regions
The different landscapes create different climates. The coast has mild Mediterranean weather. Mountains are cooler, like the Alps. The desert in the south has huge temperature swings.
| Geographic Region | Key Characteristics | Average Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| Coastal Zones | Maritime climate, fertile plains | 15-25°C |
| Atlas Mountains | Alpine terrain, snow-capped peaks | 5-15°C |
| Sahara Desert | Arid landscape, minimal precipitation | 25-40°C |
These features deeply affect Morocco’s farming, economy, and culture. Each area, from coastal plains to mountains, has its own story. They show Morocco’s beauty and strength.
Morocco’s Regional Role in North Africa
Exploring where Morocco is in Africa reveals a nation with great importance. Morocco is a key player in North African politics. It connects the continent through its economic and political power.
Morocco is a major economic force in Africa. It is a vital center for the continent’s growth. Its economy touches many areas, opening up chances for growth and development.
Economic Importance in the Region
Morocco’s economy is varied and lively. It’s known for:
- Agricultural exports
- Manufacturing sectors
- Renewable energy investments
- Advanced technology services
Political Influence Across Africa
Is Morocco in Africa? Yes, it is. The country is a big player in African politics. It works with the African Union and other groups to help the continent grow.
Trade Relations and Partnerships
Morocco’s trade reaches far and wide. It has strong ties with:
- European Union countries
- African neighboring states
- Middle Eastern economies
- North American markets
Its strategic location makes Morocco a key economic link between continents. This boosts its role in the region and worldwide.
Discovering Rabat: Morocco’s Capital City
Rabat is Morocco’s political and administrative center. It’s located on the Atlantic coast. This city shows Morocco’s rich culture and its modern dreams. Rabat gives visitors a special look at Morocco’s complex identity.
Rabat is known for its amazing landmarks:
- Hassan Tower: A stunning 12th-century minaret representing medieval Islamic architecture
- Mausoleum of Mohammed V: An impressive royal monument honoring Morocco’s past monarchs
- Kasbah of the Udayas: A historic fortress with breathtaking views of the Atlantic Ocean
The city mixes old Moroccan traditions with new city designs. Ancient medinas and modern buildings live together. Rabat’s strategic location shows Morocco’s changing character.
Visitors can see UNESCO sites, try local food, and see the mix of cultures. Rabat shows Morocco’s complex geography and culture.
Natural Boundaries and Geographical Features
Exploring Morocco’s map shows a rich landscape with diverse features. These features shape the country’s unique identity. Knowing where Morocco is located helps us see its natural boundaries.
Morocco’s geography is a mix of dramatic landscapes. These landscapes divide the region into different areas. The terrain stretches from coastal areas to mountainous interiors, showing geological diversity.
Atlas Mountains: A Geographical Backbone
The Atlas Mountains split Morocco into different zones. These mountains are a natural barrier with key features:
- Extend approximately 1,600 miles across northwestern Africa
- Create microclimates that support unique ecosystems
- Separate coastal regions from interior desert landscapes
Coastal Regions and Mediterranean Influence
Morocco’s northern and western coasts have a Mediterranean and Atlantic environment. These areas offer:
- Mild Mediterranean climate
- Fertile agricultural zones
- Strategic maritime trade routes
Sahara Desert’s Geographical Impact
The southern regions of Morocco meet the Sahara Desert. This desert changes the geography. It affects:
- Climate patterns
- Cultural practices
- Economic activities in southern regions
Understanding Morocco’s natural boundaries shows a complex geography. It defines Morocco’s unique position between continents and climates.
Morocco’s Position in Modern Geopolitics
Exploring Morocco’s place in the world reveals a key player in global politics. As a strategic African country, Morocco acts as a bridge between continents. It plays a vital role in international relations.
Morocco’s location is key to its importance. It sits at Africa’s northwestern tip, connecting Europe and Africa. This spot gives Morocco big diplomatic and economic benefits.
- Diplomatic mediator in regional conflicts
- Key trade partner for European and African nations
- Important security collaborator in North Africa
The country’s role in international relations is complex. Yes, Morocco is in Africa. But its influence goes beyond the continent. It’s a progressive African nation with global goals.
“Morocco represents a unique geopolitical intersection of African, Arab, and Mediterranean identities.” – International Relations Expert
| Geopolitical Dimension | Morocco’s Strategic Position |
|---|---|
| Continental Influence | African Union member with strong regional leadership |
| Economic Partnerships | Free trade agreements with EU and African nations |
| Security Collaboration | Counter-terrorism and diplomatic mediation hub |
Morocco skillfully navigates the world’s complex politics. It uses its location to stay a major player globally.
Conclusion
When you look into where Morocco is, you find a country that doesn’t fit into one box. Morocco is a lively African nation with deep roots and complex cultural ties. It sits at Africa’s northwestern edge, acting as a bridge between continents. This mix of African, European, and Arab influences makes it unique.
Is Morocco in Africa? Yes, it is. But its identity goes beyond just being in Africa. Its location by the Mediterranean and Atlantic coasts gives it a special view. Morocco’s varied landscapes, from the Atlas Mountains to the Sahara Desert, show its diversity and strength.
Understanding Morocco is more than just knowing where it is. It’s a country that connects different worlds, showing the blend of history, culture, and geography. Its rich heritage shows that boundaries are not as fixed as they seem.
Exploring Morocco’s complex identity helps us see a nation that connects Africa and the world. Its diverse nature calls for deeper exploration and appreciation of its geography and culture.
FAQ
Is Morocco definitively located in Africa?
Yes, Morocco is definitely in Africa. It’s in the northwestern part of the continent. It’s a key country in North Africa with great strategic value.
What countries border Morocco?
Morocco borders Algeria to the east and Mauritania to the south.
What is the capital city of Morocco?
Rabat is Morocco’s capital. It’s on the Atlantic coast. Rabat is the country’s political and administrative center, known for landmarks like the Hassan Tower and the Mausoleum of Mohammed V.
How close is Morocco to Europe?
Morocco is very close to Europe. The Strait of Gibraltar, just 14 kilometers (8.7 miles) wide, separates them. This has made Morocco a key link between Africa and Europe.
What major geographical features define Morocco?
Morocco has many geographical features. It has the Atlas Mountains, long coastlines, and the Sahara Desert’s northern edge. These features make its climate and ecosystems varied.
Is Morocco considered part of the Arab world?
Morocco is in Africa but has Arab cultural ties. It mixes African, Arab, and Berber cultures. This makes it a special place at the crossroads of Africa and the Middle East.
What ocean and sea borders Morocco?
Morocco borders the Atlantic Ocean to the west and the Mediterranean Sea to the north. These seas greatly affect its climate, economy, and history.
How does Morocco fit into African geopolitics?
Morocco is a big player in African politics. It’s one of the continent’s biggest economies. It’s part of the African Union and has strong ties with many African countries.






